Declaring a service in the manifest
<manifest ... >
...
<application ... >
<service android:name=".ExampleService" />
...
</application>
</manifest>
A services runs in the same process as the application in which it is declared and in the main thread of that application, by default. So, if your service performs intensive or blocking operations while the user interacts with an activity from the same application, the service will slow down activity performance. To avoid impacting application performance, you should start a new thread inside the service.
Intent intent = new Intent(this, HelloService.class);
startService(intent);
Stopping a service
stopService()
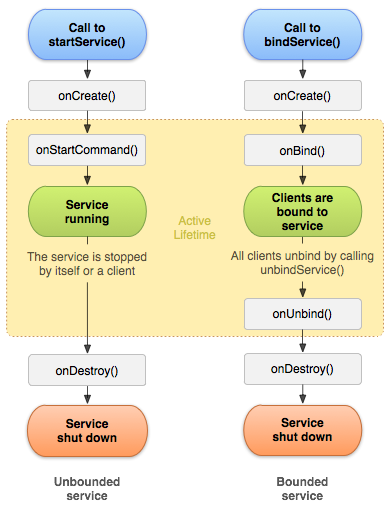
Service Lifecycle Callbacks :
public class ExampleService extends Service {
int mStartMode; // indicates how to behave if the service is killed
IBinder mBinder; // interface for clients that bind
boolean mAllowRebind; // indicates whether onRebind should be used
@Override
public void onCreate() {
// The service is being created
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
// The service is starting, due to a call to startService()
return mStartMode;
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
// A client is binding to the service with bindService()
return mBinder;
}
@Override
public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) {
// All clients have unbound with unbindService()
return mAllowRebind;
}
@Override
public void onRebind(Intent intent) {
// A client is binding to the service with bindService(),
// after onUnbind() has already been called
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
// The service is no longer used and is being destroyed
}
}